Ceratothripoides revelatus (Priesner, 1937)
Thripinae, Thripidae, Terebrantia, Thysanoptera
Figures
Fig. 1: 8-segmented antenna, pedicel, segments III and IV with forked sense cone, terminal segments V-VIII, segments III-V
Fig. 2: Head dorsal with ocellar triangle
Fig. 3: Pronotum
Fig. 4: Meso- and metanotum
Fig. 5: Meso- and metasternum
Fig. 6: Fore wing and distal region of fore wing
Fig. 7: Fore wing basal region, clavus
Fig. 8: Tergites IV and V
Fig. 9: Sternites VI and VII
Fig. 10: Tergite VIII with posteromarginal comb
Fig. 11: Tergite VIII with posteromarginal comb and tergite IX
Fig. 12: Tergites IX-XI
Introduction and recognition
Ceratothripoides revelatus damages flowers of cocoa and lemon. Both sexes fully winged. Body brown; all tarsi, apices of tibiae and antennal segment III yellow, IV-V variably yellow and brown; fore wings brown or deeply shaded. Antennae 8-segmented; segments III & IV with forked sense cone and many microtrichia, segment I with pair of dorso-apical setae (Fig. 1). Head with 3 pairs of ocellar setae, pair III very long and arising within ocellar triangle; compound eyes with no pigmented facets (Fig. 2). Pronotum with 2 pairs of elongate posteroangular setae (Fig. 3). Mesonotum anteriorly with campaniform sensilla (Fig. 4); mesosternal furca with spinula (Fig. 5). Metanotal median area with mainly equiangular reticulation or transverse at anterior, but equiangular reticulations on posterior half; median setae longer than lateral metanotal setae and arising at anterior margin; campaniform sensilla present (Fig. 4). Mid and hind tarsi 2-segmented. Fore wing first vein with about 7 setae basally and 2 setae distally; second vein with complete setal row; fore wing clavus with 5 or 6 marginal setae and one discal seta (Fig. 6 and 7). Tergites without ctenidia (Fig. 8); tergite VIII posterior margin with complete comb of long and slender microtrichia (Fig. 10 and 11); X with dorsal split (Fig. 12). Sternites III-VI with 3 pairs of marginal setae; sternite VII with S1 and S2 arising well in front of posterior margin (Fig. 9).
Male similar to female; sternites III-VII with 2 or more irregular transverse rows of small glandular areas; tergite IX with median setae slender.
Taxonomic identity
Species
Ceratothripoides revelatus (Priesner, 1937)
Taxonomic history
Taeniothrips revelatus Priesner, 1937
Common name
-
Present taxonomic position
Family: Thripidae Stephens, 1829
Subfamily: Thripinae (Stephens) Karny, 1921
Genus: Ceratothripoides Bagnall, 1918
Genus description
The genus Ceratothripoides Bagnall, 1918
This genus comprises 5 Old World species from the Africa and the Oriental region. One of these species, Ceratothripoides claratris, is recorded as a tospovirus vector on tomatoes with different levels of virulence (Premachandra et al. 2005; Halaweh & Poehling 2009). Species of Ceratothripoides have following characters: 8-segmented antennae, antennal segments III & IV with forked sense cone, antennal segment I with a pair of small dorso-apical setae, tergite VIII posterior margin with complete comb of long microtrichia, sternites III-VI with 3 pairs of marginal setae, and sternite VII with S1 and S2 arising well in front of posterior margin (Mound & Nickle 2009). All of them have a wide gap in the setal row on the first vein of fore wing, and a complete setal row on the second vein. In some cases, like Ceratothripoides claratris and Ceratothripoides cameroni discrimination is difficult and not always clear.
Species description
Typical key character states of Ceratothripoides revelatus
Coloration and body sculpture
Body color: mainly brown to dark brown
Surface of head, pronotum and fore legs: without obvious or with weakly reticulate sculpture
Antennae
Form of sense cones on antennal segments III and IV: emergent and forked on segments III and IV
Number of antennal segments: 8
Antennal segment I: with pair of small setae on dorso-apical margin
Antennal segment II: without an exceptionally long seta at the inner apex
Antennal segment II shape: symmetric
Antennal segment III shape: symmetric
Antennal segment IV and V: without a hyaline ring at the base
Antennal segment VI bears: not a remarkably dagger-shaped sensorium
Forked sense cone on antennal segment IV: scarcely extending beyond base of segment V
Length of antennal segment III and IV: antennal segment III similar in length to segment IV
Head
Distance between bases of ocellar setae III: same or less than width of first ocellus
Head: not prolonged in front of compound eyes
Ocellar setae I: present (mostly one behind the other)
Length of ocellar setae II: shorter than setae III
Ocellar setae III: arising within ocellar triangle anterior to tangent of anterior margin of hind ocelli
Ocelli: present
Length of postocular setae: not alternating short and long setae
Number of ocellar setae: 3
Compound eyes: without pigmented facets
Prothorax
Number of pairs of long anteroangular setae: 0
Number of pairs of long posteroangular setae: 2
Number of pairs of elongate pronotal setae: 2
Number of pairs of posteromarginal minor setae: 3-4
Pronotal blotch or internal apodeme: absent
Pronotum shape: broadly rectangular
Pronotum posteromarginal/posteroangular setae: S2 longer than S3, not equal in length
Mesothorax
Campaniform sensilla: present
Mesosternal furca: with median spinula
Metathorax
Metanotal campaniform sensilla: present
Metanotal median setae: S1 at anterior margin
Metanotum with dominant sculptured triangle medially: absent
Metasternal furca: without spinula
Sculpture of metanotum median area: with mainly equiangular reticulation or transverse at anterior, but equiangular reticulations on posterior half
Shape of metathoracic furca: transverse, V-shaped
Metanotal median setae length: longer than lateral metanotal setae
Wings
Fore and hind wings: present, more than half as long as abdomen (macropterous)
Fringe cilia arising: from sockets
Fore wing veins: present
Fore- and hind wing surface: covered with microtrichia
Apex of fore wing: with prominent terminal setae
Fore wing anterior margin (costal vein): with setae and cilia but cilia longer than setae
Fore wing clavus - number of discal setae: 1
Fore wing clavus - number of marginal setae: 5-6
Fore wing costal fringe cilia: arising at anterior margin of wing
Fore wing first vein: distinct from costal vein
Fore wing first vein setal row: incomplete, with setae not closely and uniformly spaced
Fore wing second vein setal row: complete, setae uniformly spaced
Fore wing shape: mainly parallel sided or margins run continuously towards each other
Fore wing surface: not reticulate
Fore wing first vein number of setae on distal half: 2
Fringe cilia on posterior margin near apex: distinctly wavy (undulated)
Length of fore wing costal setae at middle of wing: longer than half of median wing width
Fore wing extreme apex color: dark
Fore wings: uniformly dark brown or uniformly dark or shaded, but with bas or sub-base pale (rare: entirely brown, sometimes with slightly paler areas subapically, medially and sub-basally or uniformly light brown)
Legs
Fore tibia: not prolonged around fore tarsus
Mid and hind tarsi: with two segments
Color of fore tarsi: pale or yellow, sometimes apical shaded or brown
Abdomen
Pleurotergites: not covered in microtrichia
Sternite II: with marginal setae but no discal setae
Sternites IV, V and VI: with marginal setae but no discal setae
Craspedum on tergites IV to VI: absent
Sternite VII median posteromarginal setae S1: arising in front of posterior margin
Sternite VII: with marginal setae but no discal setae
Tergites II to VII median setal pair: no more than 0.3 as long as median length of tergite
Tergites IV and V median setal pair: shorter than distance between their bases
Tergites V to VII: without ctenidia laterally, but sometimes with rows of microtrichia
Surface of lateral thirds of abdominal tergites: without regular rows of fine microtrichia
Tergite VIII ctenidia: without paired ctenidia laterally, sometimes with irregular microtrichia
Tergite VIII posteromarginal comb of microtrichia: present and complete medially
Tergite VIII shape of posteromarginal microtrichia: long, slender and irregular or regular
Tergite X: not tubular, longitudinally incomplete
Setae on abdominal tergite X: all setae slender
Similar or related species
Ceratothripoides revelatus is very similar to Ceratothripoides brunneus. Compared to other species of that genus, both species have brown or deeply shaded fore wings and compound eyes with no pigmented facets (Ceratothripoides cameroni and Ceratothripoides claratris have uniformly pale fore wings and compound eyes with 4 to 5 weakly pigmented facets). Furthermore, in Ceratothripoides cameroni and Ceratothripoides claratris ocellar setae III arising on anterior margin of ocellar tiangle and the distance between bases of ocellar setae III greather than width of first ocellus (in Ceratothripoides revelatus always less than width of first ocellus; in Ceratothripoides brunneus less, same or greater than width of first ocellus; both with ocellar setae III arising within ocellar triangle). Ceratothripoides revelatus differs from Ceratothripoides brunneus in having the metanotal median area mainly with equiangular reticulation, meso- and metanotum with campaniform sensilla, and the fore wing clavus with 5 or 6 marginal setae and 1 discal seta. Whereas Ceratothripoides brunneus has sculptured lines on metanotum transverse at anterior and irregular equiangular reticulations on posterior half, meso- and metanotum without campaniform sensilla, and the fore wing clavus with 6 or 7 marginal setae but no discal seta. The other two species (Ceratothripoides cameroni and Ceratothripoides claratris) exhibit the following characteristics: the meso- and metanotum without campaniform sensilla, and the fore wing clavus with 5 or 6 marginal setae and no discal seta.
Species of Ceratothripoides are similar to species of Craspedothrips, Diarthrothrips coffeae, Lefroyothrips pictus, Megalurothrips sjostedti and Tenothrips frici in having 8-segmented antennae with forked sense cone on segments III and IV and 2 pairs of elongate pronotal setae posteroangularly, in lacking ctenidia laterally on tergites V-VIII and regular rows of fine microtrichia on lateral thirds of tergites. Species of Ceratothripoides as well as Lefroyothrips pictus differ from other species by the complete posteromarginal comb of slender microtrichia on tergite VIII, whereas other species have a continuous craspedum (Craspedothrips hargreavesi), no comb of microtrichia (Craspedothrips xanthocerus, Diarthrothrips coffeae) or a comb of short microtrichia only laterally on posterior margin of tergite VIII (Megalurothrips sjostedti and Tenothrips frici). Compared to Lefroyothrips pictus with distinctly bicolored body color, antennal segment I without any setae on dorso-apical margin, metanotal median area scarcely sculptured on posterior half, and median pair of marginal setae on sternite VII arising at margin, species of Ceratothripoides with usually uniformly brown body color, antennal segment I with a pair of small setae on dorso-apical margin, metanotal median area always sculptured with equiangular reticulations on posterior half, and median posteromarginal setae on sternite VII arise always in front of margin. Furthermore, species of Ceratothripoides have the fore wings usually uniformly brown or uniformly pale or yellow, compared to Lefroyothrips pictus with banded fore wings.
Biology
Life history
As with other thrips species the life cycle from egg to adult is dependent on temperature. The full cycle can take less than a week to over a month and adults may live for more than one month producing several generations in one year depending on seasonal weather (Lewis 1973).
Host plants
Crops: banana, cocoa, lemon, papaya, passion fruit, tomato.
Weeds: Nerium sp.
Vector capacity
None identified, but possible mechanical distribution of phytopathogenic fungi and bacteria.
Damage and symptoms
-
Detection and control strategies
-
Additional notes
Breeding in flowers.
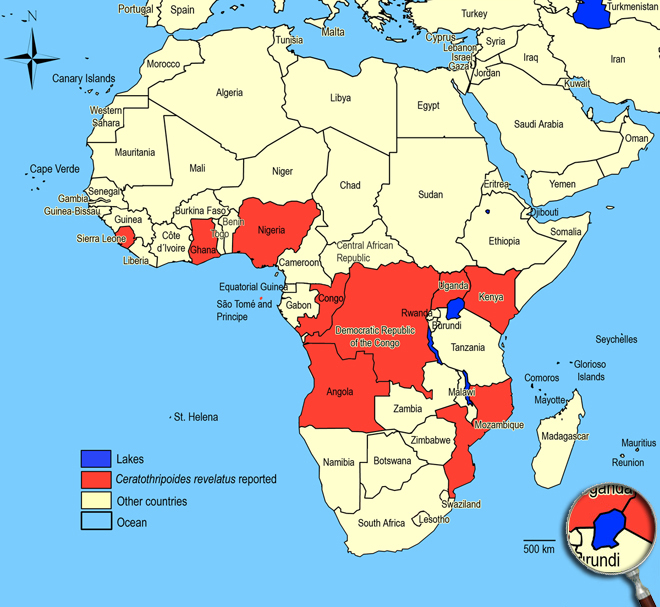
Biogeography
Africa. Angola,
Congo (Rutshuru),
Ghana (Tafo),
Kenya (Nairobi),
Mozambique,
Nigeria (Ibadan),
São Tomé,
Sierra Leone (Njala),
Uganda (Kampala, Kasese).
African countries where Ceratothripoides revelatus has been reported
Occurence of Ceratothripoides revelatus in East Africa
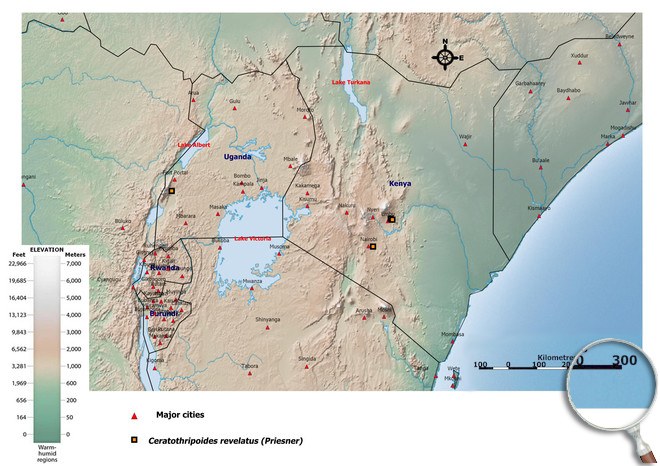
Please click here for survey sites of all observed thrips species of Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda.
Click here for locations of Ceratothripoides revelatus in parts of East Africa.
Bibliography
Faure JC (1962). Thysanoptera of Africa - 8. Revue de Zoologie et de Botanique Africaines. 66 (1-2): 165-183
Halaweh N & Poehling H-M (2009). Inheritance of vector competence by the thrips Ceratothripoides claratris (Shumsher) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Journal of Applied Entomology 133: 386-393
Lewis T (1973). Thrips: their biology, ecology and economic importance. Academic Press Inc., London Ltd., 349 pp
Mound LA & Nickle DA (2009). The Old-World genus Ceratothripoides (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) with a new genus for related New-World species. Zootaxa. 2230: 57-63
Premachandra DWTS,
Borgemeister C,
Maiss E,
Knierim D &
Poehling H-M (2005). Ceratothripoides claratris, a new vector of a Capsicum chlorosis virus isolate infecting tomatoes in Thailand. Phytopathology 95 (6): 659-663
Priesner H (1937). Neue Thysanopteren aus Zentral-Afrika. Revue de Zoologie et Botanique Africaines. 30 (1): 169-180
----
Web links
Mound´s Thysanoptera pages
Thysanoptera Checklist
ICIPE Thrips survey sites
UNI Halle & Thrips sites
Thrips of California